
Sleep apnea and how it is associated with Obesity
Sleep apnea refers to a condition in which
59,018 total views, 141 views today
Home » Role of Diet in Non-Surgical Weight Loss Procedures
Dietary modifications, along with regular exercise, play an important role in weight loss, with or with the help of surgical or non-surgical procedures. The dietary changes mainly include eating the right amount of nutrients, protein, and fibre.
Weight loss as a whole requires you to be committed and determined to the lifestyle changes. This is particular for non-surgical weight loss procedures. The procedures are only a medium which help you to start your weight loss journey, whereas as a healthy diet is required to lose additional weight and to keep it off. Let’s understand a little more about the non-surgical weight loss procedures and the role of diet.
What is Non-Surgical Weight loss?
Non-surgical weight loss procedures like endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG), are options for people who want to lose weight but are unable to due to obesity or do not qualify for surgical weight loss procedures.
Non-surgical weight loss is an option for individuals who:
Advantages of Non-surgical weight loss includes:
Non-surgical weight loss procedures are considered to be a promising new option for weight loss.
Role of Diet in Non-Surgical Weight Loss Procedures
Non-surgical weight loss procedures such as endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty and intragastric balloon surgery help patients reduce their food intake while also increasing their feeling of fullness. They produce an effect by either shrinking your stomach or inserting a saline-filled silicon balloon into your stomach.
After undergoing non-surgical weight-loss procedures, you may be put on a strict diet. Starting with a liquid diet, and then moving onto semi solid or soft foods, and then solid foods. After recovering from the procedure, you will be advised to follow a diet that emphasizes healthy, nutritious foods for you to achieve and maintain the best results.
Some tips to keep in mind after the procedure:
Tips for non-surgical weight loss procedures
Here are some tips for maintaining the lost weight through healthy eating and potentially lowering carbs, with the goal of:
This means planning your meals to be low in carbohydrates and low in calories.
Eat protein, fat, and vegetables
Protein
Protein consumption improves cardiometabolic risk factors, appetite, and body weight. Eating a protein-sufficient diet helps you feel full and reduces cravings.
Healthy protein sources include:
Healthy Fats
Include healthy fats in your diet. Avocado and olive oils are some of the healthy fats.
Because of their higher saturated fat content, other fats such as butter and coconut oil should be used in moderation.
Vegetables
Always fill your plate with leafy green vegetables that are low in calories and carbs. Include broccoli, spinach, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, tomatoes, kale, cabbage, lettuce, and cucumber in your diet. Also include a small portion of complex carbohydrates, like whole grains.
Move your body
Exercise can assist you in losing weight quickly. Lifting weights has numerous advantages. Lifting weights allows you to burn a lot of calories while also preventing your metabolism from slowing down.
Diet and exercise work together to help you lose weight and keep it off. Non-surgical weight loss procedures are safer and encourage long-term weight loss when compared to the harmful side effects linked with surgical weight loss procedures. Although, these procedures work, they need to be part of a continuum with food intake to show continued results. Diet does not play a direct role in the non-surgical weight loss but supports the results of the procedure.
If the recommended permanent lifestyle changes are not followed, you can regain the lost weight. This may require revision surgeries, adding on to the efforts made, cost, and impacting your health. Sticking to a healthy diet regime can go a long way and help you live a healthy life.
The non-surgical weight loss options at our facility include Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty, which shrinks the size of your stomach, and Intragastric Balloon Surgery, which involves inserting a saline-filled silicone balloon into your stomach. These procedures assist you by reducing your food intake and hastening the feeling of fullness.
A person’s chances of undergoing weight loss surgery are influenced by a variety of factors. Your doctor will be the best person to advise you on the type of surgery you should have.
Reference:

Sleep apnea refers to a condition in which
59,018 total views, 141 views today

Since the beginning of 20th century, the overall
58,995 total views, 141 views today

New year is the time for new beginnings.
59,694 total views, 140 views today

Weight loss can be tricky business, as it
59,566 total views, 141 views today

According to a recent study, weight loss through
60,465 total views, 141 views today

According to a recent study, preoperative very low
60,466 total views, 141 views today
A recent study conducted on GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux
60,470 total views, 141 views today
A recent study done to examine the long-term
59,348 total views, 137 views today

Overweight and obesity is a major health concern
29,611 total views, 99 views today

A recent study published in the Journal of
28,801 total views, 99 views today
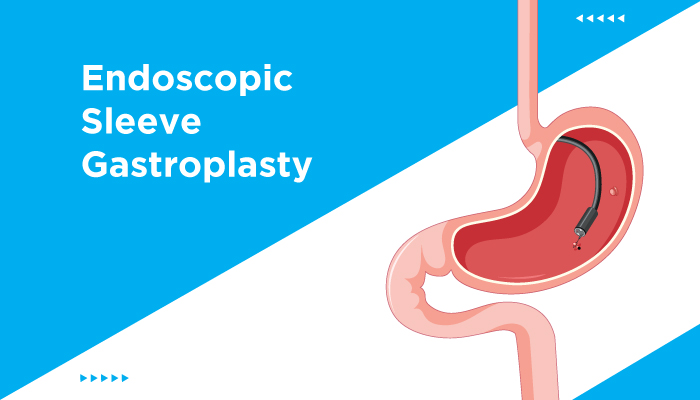
The findings from a recent study, published in
29,042 total views, 99 views today

The findings of a recent study, published in
29,442 total views, 99 views today
